Financial Ltd
|

Directory Enquiries

Currency Converter

Train Tickets



|
| |
Which Windows NT Domain
model best fits your business needs?
Are you trying to decide which domain model to use with your Windows NT
system? Do you need to know the hardware requirements for use with your new
domain model? In this article, I'll examine the four primary domain models,
server roles, trust relationships, and PDC/BDC hardware requirements.
Before we begin, some definitions To help everyone understand what is being
discussed in this article, I will define a few of the terms that I will be
using.
| Domain |
A domain is a grouping of computers, users, and resources
into groups |
| Domain Model |
A domain model extends the core coverage to include the
words and concepts needed for a particular application. In a database,
the domain model must also supply the correspondence between the
database relations and the linguistic concepts and predicates. |
| Trust Relationship |
A trust relationship describes the interaction between
domains. A machine in one domain "trusts" the authority of
another domain's directory database. |
The different types of domains
One of the first considerations when setting up a Windows NT-based
network is the domain structure. Because of the architectural limitations
inherent in the NT domain model, certain circumstances require that simple
domains be split into multiple domains connected by trust relationships, which
allow users in one domain to access resources in another.
In any domain model, a computer running Windows NT Server can participate in one
of three roles. They are as follows:
 |
Primary
domain controller (PDC): The PDC contains the master copy of the
security accounts manager (SAM) database. Each domain allows only one
PDC. |
 |
Backup
domain controller (BDC): A BDC contains a copy of the security
accounts manager (SAM). If a PDC fails, the BDC can be promoted into
the PDC slot. Microsoft Premier Support recommends having at least one
BDC per domain. |
 |
Domain
server (or resource server): A domain server can act as a file,
print, applications, or communications server. However, the domain
server can't authenticate users. |
The four primary domain models
Domain models consist of one or more of the controllers mentioned in the
previous paragraph, and use trust relationships to interact with other domains.
They are as follows:
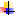 |
Single
domain model: A single PDC, along with its BDCs and resource servers,
serves the needs of the entire organization. This particular domain
model provides the easiest upgrade path to Windows 2000 and the Active
Directory. |
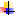 |
Single
domains with trust: This model involves two or more independent
domains, each of which is in a two-way trusting relationship with
every other domain in the organization. |
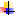 |
Single
master domain: Like the single domain with trust, the single master
domain involves at least two domains, but in this case, one domain
serves as the master and the remaining domains trust the master
domain. |
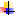 |
Multiple
master domains: This model is a hybrid of the single domain with trust
and the single master domain. |
Making a choice on your organization's needs
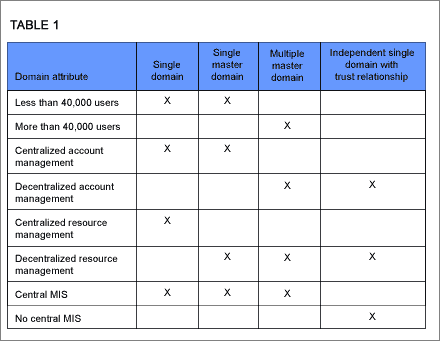
When deciding which model to use, a consideration must be made regarding
physical limitations. Every Windows NT 4.0 domain can contain 40,000 users
maximum, and the recommended size limit for the SAM database is 40 MB. Below you
will find Table 1 to help you determine which domain model best suits your
organization's needs.
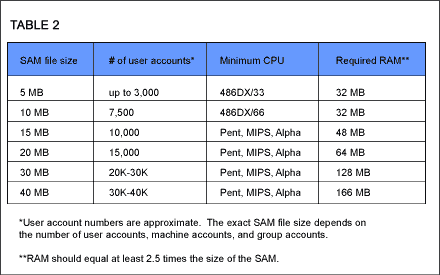
Hardware requirements for PDC/BDCs
When choosing a computer for use as a PDC, use the hardware guideline in
Table 2, seen below. The data in the table assumes three things: first, the
computer will function only as a PDC; second, no other major Windows NT
operations occur, such as SQL Server, SNA Server, and RAS operations; and third,
the computer's page file size is at least 250 MB.
|

